Table Of Contents
The Mindful Journey: Unraveling the Secrets of Weight Loss Through Awareness
The path to weight loss is often viewed through a lens of sweat, numbers, and strict diets. But what if there were a path less traveled, a route paved with the wisdom of the mind, understanding, and self-compassion? It’s a pathway that isn’t just about shedding pounds but shedding old habits, misconceptions, and mental barriers that often hold us back. This is the mindful path, and it’s navigated with the guidance of cognitive behavioral therapy weight loss apps – now, all within the palm of your hand.
Welcome to the 10 best CBT weight loss apps review! These digital companions are designed to coach you on a transformative road where mindfulness, self-awareness, and behavior modification become your trusty travel partners.App CBT Approach & Techniques UI/UX Meal Planning & Tracking Integration with Fitness Tools Community & Support Features Price & Subscription Options 1. Lasta ★★★★★ ★★★★★ ★★★★★ ★★★★☆ ★★★★★ Subscription 2. Bloom ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★★☆ Subscription 3. Shutterbite ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Free/Paid 4. Mindful Eating Coach ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Free/Paid 5. BetterMe ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Subscription 6. UnDiet Your Mind ★★★★☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★☆☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Free/Paid 7. Rise Up + Recover ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★☆☆☆ ★★★★☆ Free 8. Noom ★★★★★ ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ ★★★★☆ Subscription 9. Eat Right Now ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★☆☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Free/Paid 10. MEAL ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★★☆☆ ★★☆☆☆ ★★★☆☆ Free/Paid
Top 10 CBT Weight Loss Apps: Transforming Your Mind and Body
1. Lasta
- Rating: 9.8/10
- Award: Best Overall CBT Weight Loss App
- Nominations: Holistic Approach to Weight Loss, Superior User Experience
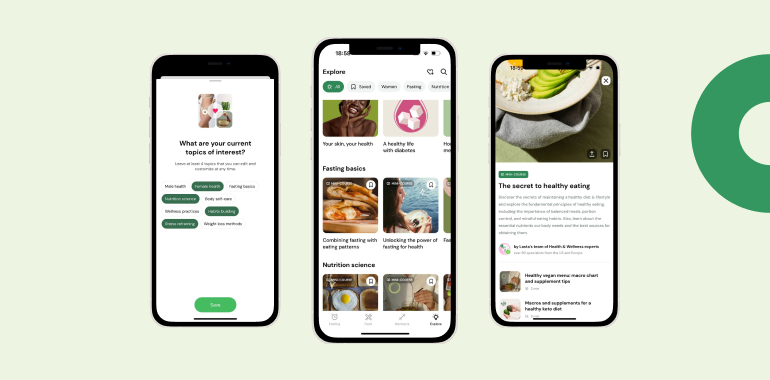
With Lasta stands tall as a comprehensive assistant in one’s weight loss and overall wellness journey. Integrating the principles of cognitive behavioral therapy with weight loss strategies, Lasta promotes a holistic approach to health.
CBT Psychology
Lasta offers a 30-day guided course on CBT and healthy living. There’s also a library filled with meditation tracks and various audio formats, and content summaries. These resources act as fuel for the mind, encouraging individuals to learn, grow, and succeed.
Inclusive Weight Loss Program
Catering to different genders and dietary preferences, Lasta prides itself as an inclusive platform, mainly focusing on women’s wellness.
Customizable Meal Plans
Whether Keto, Paleo, Vegan, or anything in between, Lasta’s expert nutritionists and chefs can create a meal plan that suits you best.
Mindful Eating Practices
The app doesn’t just stop telling you what to eat; it guides you on how to eat. With mindful chewing and savoring techniques, you’re encouraged to slow down and truly appreciate your food.
24/7 Customer Service
Lasta believes in maintaining a continuous relationship with its users, providing round-the-clock customer support through email.
Strengths
- Versatile Content Format: Learning comes in different styles; audio, written summaries, and guided exercises all cater to varied learning preferences.
- Diverse Meal Options: From Keto to Vegan, the meal planning feature ensures no one is left out.
- Focus on Mindfulness: Integrating mindful eating exercises is a unique approach that sets Lasta apart from other weight loss apps.
Weaknesses
- Accessibility for Non-English Speakers: Currently available only in English, it may not cater to a global audience.
- Subscription Cost: Although providing excellent value, the app is not accessible, which might be a barrier for some potential users.
2. Bloom
- Rating: 9.7/10
- Award: Top Mindfulness Integration
- Nominations: Excellent Meditation Tools, Personal Growth Focus
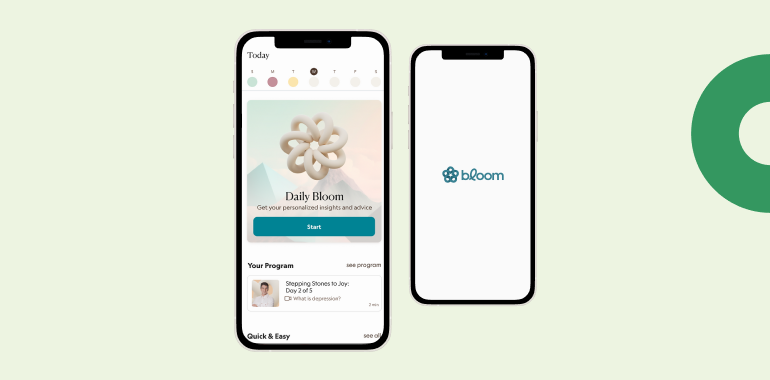
Bloom has established itself as a gentle guide to a healthier you in a world where weight loss often turns into a relentless pursuit of shedding pounds.
CBT Approach
Bloom’s focus on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy sets the tone for a balanced and mindful weight loss journey. The app includes interactive therapy sessions, journaling exercises, and expert-led webinars.
Personalized Plans
Bloom offers meal plans and exercise routines that cater to your unique body type and preferences. Its algorithm constantly learns from your feedback and adjusts the plan accordingly.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Bloom guides you through daily mindfulness exercises and meditation practices, helping you build a connection between body and mind.
Strengths
- Holistic Approach: By integrating mental well-being with weight loss, Bloom nurtures body and soul. It’s a cbt app for weight loss with a free option!
- Dynamic Adaptation: Personalized plans that adapt to user feedback create a truly individualized experience.
- A Sense of Community: A robust community forum fosters user connections, creating a supportive environment.
Weaknesses
- Limited Offline Capabilities: Lack of offline content can be a drawback for those without constant internet access.
- Premium Content Restrictions: Some of the best features hidden behind a paywall may deter potential users.
- Complex Interface for Some Users: A rich feature set may confuse some beginners.
3. Shutterbite
- Rating: 9.5/10
- Award: Most Innovative Visual Approach
- Nominations: Unique Image-Based Journaling, Effective Visual Cues
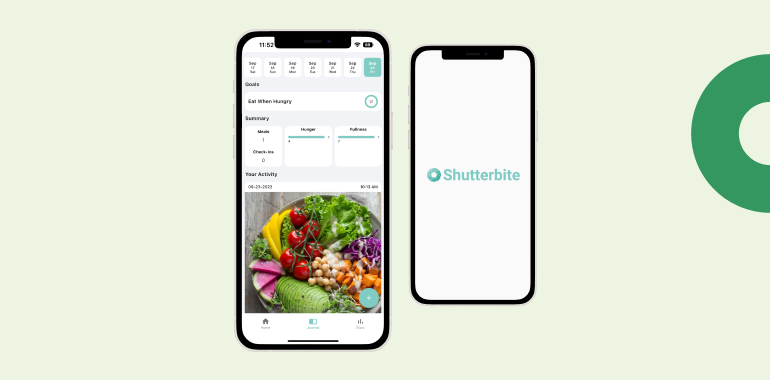
Shutterbite, a name that intrigues and inspires, has emerged as an avant-garde tool in the realm of weight loss and mindful eating.
Photographic Food Journaling
Shutterbite enables users to photograph their meals and document their emotions, fostering awareness about eating habits.
Virtual Nutritionist
An AI-driven virtual nutritionist helps users navigate their meal choices, offering real-time advice and feedback.
Mindful Eating Challenges
Engaging challenges encourages mindful eating practices, such as savoring each bite and practicing gratitude for food.
Strengths
- Visual Engagement: By combining photography with weight loss, Shutterbite taps into the visual nature of today’s digital culture.
- Emphasis on Mindfulness: Shutterbite takes users beyond mere calorie counting and emphasizes a mindful appreciation of food.
- Interactive Community: The social sharing feature promotes a sense of camaraderie and accountability.
- Cross-platform Accessibility: Available on multiple devices, Shutterbite ensures that your weight loss journey is always at your fingertips.
Weaknesses
- In-App Purchases: Additional content and advanced sessions require payment, limiting access for some users.
- May Not Cater to Non-Tech-Savvy Users: The photographic element may alienate those not comfortable with technology.
4. Mindful Eating Coach
- Rating: 9.3/10
- Award: Best Mindful Eating Practices
- Nominations: Expert Coaching, Customized Mindful Exercises

Mindful Eating Coach app takes a different bite out of the weight loss pie, focusing on the quality of your relationship with food rather than just the quantity of calories.
Mindfulness Practices
The app guides you through various mindful eating techniques to help you savor and appreciate your food.
Personalized Coaching
A built-in coaching feature tailors the experience to your individual needs and goals.
Emotion and Eating Tracking
Connecting emotional states with eating patterns allows for deeper insights and self-awareness.
Progress Tracking
Monitor your growth through easy-to-understand progress charts and insights.
Strengths
- Unique Mindfulness Approach: It distinguishes itself by offering guided mindfulness exercises tailored to eating habits.
- Personal Touch: The personalized coaching feature creates a customized experience, making the journey feel intimate and catered to the individual.
- Emotion-Driven Insights: Linking emotions with eating patterns provides a rich layer of understanding that goes beyond traditional dieting.
Weaknesses
- Limited Free Content: Some users may find the content restrictions on the free version limiting, potentially hindering the full exploration of the app.
- Simplicity Might Not Suit Everyone: While some appreciate the app’s minimalistic design, others may desire more comprehensive features.
5. BetterMe
- Rating: 9.2/10
- Award: Best Fitness & Mental Wellness Combo
- Nominations: Comprehensive Workouts, Balanced Meal Plans
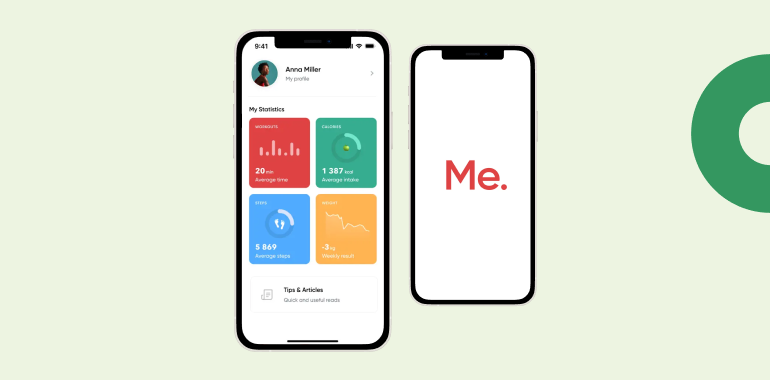
BetterMe stands out with its emphasis on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and mindfulness. This app is not just a typical weight loss tool but a comprehensive guide, steering users through a journey that intertwines physical and mental well-being.
Personalized Meal Plans
With an emphasis on mindful eating, BetterMe crafts meal plans that align with user preferences and dietary needs.
Meditative Guides
The app incorporates daily meditation and relaxation sessions to reduce stress, often linked to unhealthy eating habits.
Progress Tracking
BetterMe offers easy-to-use tools for users to track their weight loss, including visual graphs, dietary logs, and fitness milestones.
Strengths
- Mind-Body Connection: BetterMe’s integration of CBT and mindfulness techniques goes beyond physical health, addressing the mental aspect of the weight loss journey.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed with the user in mind, the app is reflexive and painless to navigate, making it suitable for people of all tech levels.
- Comprehensive Approach: From diet to exercise to mental health, BetterMe offers an all-encompassing weight loss solution.
Weaknesses
- Subscription Model: While BetterMe provides a robust set of features, many come at a premium cost, which could be a deterrent for some.
- Generalized Meal Plans: Although the app offers tailored meal plans, they might not cater to all specific dietary restrictions and needs.
Also, read – Lasta Vs. Betterme Review
How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Revolutionizes Weight Loss
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT as we’ll affectionately call it, is like a wise old wizard in the mental health field. Primarily known for treating conditions like anxiety and depression, this magical method has found a new partner in crime – the mission to lose weight.
The CBT app for weight loss is like a fascinating journey through the labyrinth of your mind. It helps you recognize and challenge negative thoughts, replacing them with positive, empowering beliefs.
Now, apply this to weight loss. Those nasty thoughts that say, “I can’t lose weight” or “I’ll never be healthy” are banished, making room for positive affirmations.
According to studies in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, CBT profoundly impacts weight loss. Participants who engaged in this approach found themselves not just lighter in body but also in spirit.
Also, read – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: What Does Cbt Stand For?
Why CBT Apps Are Game-Changers for Sustainable Weight Management
First off, let’s talk about the connection between our thoughts and our bodies. Ever seen how your mood can influence your cravings? Or how stress might lead to some not-so-healthy eating habits? You’re not alone! This is where psychology plays a noteworthy role in weight loss.
Imagine combining this psychological wisdom with the convenience of your smartphone. Weight loss apps are like having a personal nutritionist, fitness trainer, and motivational coach all in one! Let’s see how it all works:
Personalized Goals
These apps typically start by getting to know you. They ask about your habits, preferences, and what you want to achieve. It’s like having a friendly chat with a wellness expert who genuinely wants you to succeed.
Mindful Eating Techniques
The best CBT app needs to offer tools to help you understand why you eat rather than just what you eat. These apps can help you identify those triggers and manage them more healthily.
Motivation and Rewards
These apps offer encouragement through virtual badges, uplifting messages, and sometimes real-life rewards.
Social Connection
Some apps also have community features to connect with others on the same journey. Share your triumphs, your challenges, and get support from fellow others.
Track and Analyze
With easy-to-use tracking features, you can monitor your progress, analyze your habits, and see how far you’ve come.
Expert Guidance
Many weight loss apps offer access to professionals like dietitians, psychologists, and fitness trainers.
Also, read – How to Find Motivation to Lose Weight
6. UnDiet Your Mind
- Rating: 9.1/10
- Award: Most Transformative Mindset Change
- Nominations: Intuitive Eating Guidance, Emotional Health Support
It’s a revolution in thinking, a paradigm shift that takes you away from the rigidity of dieting and into a space of mindfulness, acceptance, and balance. This Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) oriented app carves a mindful path to a slimmer you, transforming the weight loss journey into a holistic self-discovery expedition.
Mindful Eating Practices
With guided exercises and daily mindfulness challenges, the app supports the development of conscious eating habits.
Personalized Coaching
Available 24/7, trained coaches work closely with users, offering support, encouragement, and tailored advice.
Emotional Well-Being Tools
The app provides resources for managing stress and anxiety, focusing on overall emotional health as part of the weight loss journey.
Strengths
- Holistic Approach: UnDiet Your Mind transcends the physical aspects of weight loss and focuses on emotional well-being, setting it apart.
- Accessibility: Its user-friendly interface and availability on various platforms make the app accessible to a broad audience.
- Real Human Interaction: Personalized coaching adds a human touch to the app, enhancing user engagement and support.
Weaknesses
- Limited Free Content: While offering rich content, many features are locked behind a subscription, limiting access for users on a budget.
- May Not Suit Everyone: The non-traditional approach may need to align with those looking for strict dieting plans and structured routines.
7. Rise Up + Recover
- Rating: 8.9/10
- Award: Best Recovery-Focused App
- Nominations: Support for Eating Disorders, Positive Community
Rise Up + Recover is a psychological weight loss app designed to assist users in recovering from eating disorders and embracing a mindful approach to living. By blending Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques with empathy, this app lays down pathways that lead to a healthier relationship with food and oneself.
CBT-Based Tools
Guided exercises, reflections, and journaling features help users understand their thought patterns and behaviors regarding food.
Meal Logging with Emotions
Users can log meals and associate emotions with each entry, fostering mindfulness and self-awareness.
Recovery Goals and Reminders
Personalized goal setting and daily reminders encourage users to stay committed to their recovery journey.
Expert Resources
Access to educational articles, podcasts, and videos from mental health professionals offers robust support and information.
Strengths
- Specialized Focus: It specifically targets individuals recovering from eating disorders, providing specialized support.
- Emphasizes Emotional Wellness: The app encourages users to explore their emotional relationship with food.
- Professional Insight: Access to expert resources ensures that users are guided by credible and professional advice.
Weaknesses
- May Not Suit Traditional Dieters: The app’s specialized focus may not align with those seeking typical weight loss routines and diet plans.
- Potential Trigger for Some Users: Although designed to aid recovery, some content might be triggering for individuals with certain types of eating disorders.
8. Noom
- Rating: 8.8/10
- Award: Top Behavior Change Techniques
- Nominations: Personalized Coaching, Science-Backed Strategies
Noom emerges as a forerunner, wielding the power of psychological insight to foster a comprehensive, mindful weight loss journey. This innovative platform doesn’t merely offer users a diet; it delves deep into the psyche, guiding users to understand the “why” behind their habits and decisions.
Psychology-Driven Approach
Rooted in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Noom assists users in recognizing and transforming negative thought patterns and habits.
Dynamic Coaching
Real-time coaching with trained professionals ensures users have guidance and support throughout their Noom experience.
Engaging Content
Daily articles, challenges, and quizzes keep users informed and engaged, making weight loss an enlightening journey.
Strengths
- Deep Behavioral Insight: Noom’s foundation in psychology offers users a unique approach to weight loss, addressing underlying behaviors and thought patterns.
- User-Centric Design: The app is designed with vibrant colors and an intuitive interface, ensuring an engaging and user-friendly experience.
- Evidence-Based: Noom is grounded in scientific research, with its approach being rooted in evidence-based practices.
Weaknesses
- Subscription Cost: While Noom provides a plethora of features, its premium offerings come with a notable price tag, potentially limiting accessibility for some.
- Automated Responses: Some users have expressed that interactions, especially with coaches, sometimes feel automated and lack a personal touch.
Also, read – Lasta Vs. Noom Review: Navigate the best choice for you!
9. Eat Right Now
- Rating: 8.7/10
- Award: Best for Craving Management
- Nominations: Real-Time Support, In-depth Craving Analysis

Eat Right Now stands as a beacon for those weary of the conventional dieting approach, using cognitive behavioral therapy to guide its users toward a more mindful understanding of food, hunger, and satisfaction.
Mindfulness Training
The app offers daily mindfulness practices to cultivate awareness around eating habits, cravings, and sensations.
In-Depth Analysis
Analyzing triggers and responses to cravings, the app helps users understand why they eat, rather than merely what they eat.
Expert-Led Guidance
With Dr. Brewer’s scientific expertise, the app offers a scientifically-backed approach to mindful eating.
Interactive Exercises
Engaging videos and quizzes allow users to actively participate in their mindfulness training.
Strengths
- Genuine Mindfulness Focus: The app’s emphasis on mindfulness sets it apart from traditional diet-focused apps, offering a more profound and sustainable change.
- Accessible and Engaging Content: The integration of videos, quizzes, and interactive content makes the app engaging and user-friendly.
Weaknesses
- May Require a Shift in Mindset: The focus on mindfulness rather than traditional dieting might not appeal to all users, especially those looking for quick, tangible results.
10. MEAL
- Rating: 8.5/10
- Award: Most User-Centric Meal Planning
MEAL (Mindful Eating And Living) offers a refreshingly different perspective. It emphasizes a holistic and mindful approach to nourishment, encouraging users to embrace not only healthy eating but also a conscious lifestyle.
Mindfulness Practices
MEAL integrates meditation and mindfulness techniques, promoting a balanced relationship with food.
Mindful Eating Exercises
Unique exercises like mindful chewing encourage users to slow down and truly savor their meals.
Emotional Tracking
Connecting emotions with eating habits helps users identify patterns and triggers that may affect their food choices.
Strengths
- Holistic Approach: MEAL transcends mere diet planning, incorporating mindfulness practices for a well-rounded wellness experience.
- Flexibility: The app’s customizable meal plans cater to various dietary preferences and requirements, ensuring inclusivity.
- Emphasis on Emotional Awareness: By linking emotions to eating habits, MEAL offers insight into deeper behavioral patterns.
- Strong Sense of Community: The communal aspect fosters a supportive environment, enhancing motivation and connection.
Weaknesses
- Potential Learning Curve: Some users may find the combination of mindfulness practices and meal planning initially overwhelming.
- Subscription Costs: Access to the full range of features requires a subscription, which might be a barrier for some users.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Successful Weight Loss
The mind-body connection is a powerful force in weight loss. When you understand the psychological principles behind your eating habits, you gain control over them. Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on identifying negative thought patterns and replacing them with healthier alternatives.
Many of us eat in response to emotional triggers rather than physical hunger. CBT helps identify these triggers and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Through consistent practice, these new habits become automatic, creating lasting change.
Self-monitoring is another key psychological mechanism. By tracking food intake, emotions, and physical activity, you become more aware of patterns and can make intentional choices. This awareness is the first step toward change.
Goal-setting provides direction and motivation. Effective goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Small, achievable goals build confidence and momentum, leading to larger transformations over time.
Key Features to Look for in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Weight Loss Apps
When choosing a psychological weight loss app, certain features can enhance your experience and increase your chances of success. Here are the key elements to consider:
- Evidence-based approach: Look for apps grounded in cognitive behavioral therapy principles with scientific backing.
- Personalization options: Your journey is unique, so the app should adapt to your specific needs and preferences.
- Comprehensive tracking tools: Effective apps allow you to monitor food intake, emotions, physical activity, and progress toward goals.
- Mindfulness exercises: Guided practices help develop awareness around eating habits and emotional triggers.
- Educational content: The app should provide information about the psychology of eating and weight management.
- Support systems: Community features or coaching options provide accountability and encouragement.
- User-friendly interface: The app should be intuitive and easy to navigate to encourage consistent use.
How to Choose the Right Psychological Weight Loss App for Your Needs
With so many options available, finding the right CBT app for weight loss can feel overwhelming. Start by identifying your specific goals and challenges. Are you struggling with emotional eating, portion control, or maintaining motivation? Different apps excel in different areas.
Consider your personal preferences and learning style. Do you prefer a more structured approach with daily lessons, or do you want flexibility to explore content at your own pace? Some apps focus on visual elements, while others emphasize text or audio.
Think about your budget and how much you’re willing to invest. While many apps offer free versions, premium features often require a subscription. Evaluate whether the additional benefits justify the cost for your situation.
Read user reviews and check ratings, paying particular attention to comments from people with similar goals. Many apps offer free trials, allowing you to explore the interface and features before committing. I recommend trying 2-3 options to find the best fit for your needs.
Beyond Weight Loss: Mental Health Benefits of CBT Apps
The benefits of CBT weight loss apps extend far beyond the number on the scale. Users often report improved self-esteem and body image as they develop a healthier relationship with food and their bodies. Rather than viewing themselves through the lens of weight alone, they begin to appreciate their bodies for what they can do.
These apps teach stress management techniques that can be applied to all areas of life. By identifying triggers and developing healthy coping mechanisms, users experience reduced anxiety and improved emotional regulation. The mindfulness practices included in many apps help users stay present and make conscious
My name is Barbara Kovalenko. I hold a Bachelor's degree in Human Nutrition from Bogomolets National Medical University in Ukraine and a Master's degree from Boston University in the United States. Over the past few years, I have gained valuable experience as a nutritionist and have since decided to share my knowledge and expertise with a wider audience. Currently, I am working as a nutritional consultant with the Lasta app.










Thank you for this detailed description of the pros and cons of cbt weight loss app. It is really helpful.
Hi, Karina👋
Thank you so much for your feedback!