Table Of Contents
Many have heard of the Keto diet, but what does “keto” mean?
So, What Is Ketosis
Ketogenesis definition is a metabolic state in which the body burns fat instead of glucose (carbohydrates) for energy. This happens when the body reaches a deficit in carbohydrates (from dieting or other deficiency), and in the process, ketones are created. These ketones, produced by chemicals in the liver, are sent through the bloodstream for muscles and other tissues to use as fuel.
What Happens in Ketosis? – Reaction in Your Body
In short, ketosis occurs when the body does not have enough carbs, so it uses stored fats for energy. This process is standard in people with diabetes, as it can occur if the body is insulin-deficient or cannot correctly utilize insulin.
Stages of Ketosis
Ketosis is defined by three stages:
- Getting into ketosis
One way of initiating deep ketosis includes fasting. Fasting helps start ketosis (typically in three days), in which the body begins to burn the remaining glucose and begins the process of carb reduction. Intermittent fasting is recommended to ease into ketogenic food while fasting burns the remaining glucose. This is because intake is restricted to a cycle (usually an 8-hour window of food intake and a 16-hour window of fasting).
- Keto-adaption
In this stage, it is essential to maintain daily activities including exercise to help the body build up to the fat-burning mode.
- Metabolic flexibility
This stage focuses on maintaining ketosis through a fast-forward keto diet, exercise, and reduced carb intake. Once you’ve reached metabolic flexibility, this consistency can limit the body’s responses when encountering small amounts of foods/nutrients outside the keto diet, thus maintaining the ketogenic process.
How Many Days Does It Take to Get into Ketosis?
Getting into a state of ketosis is a process that everyone’s body adapts to differently. While some people might keto-adapted in as little as 2 or 3 days, others can take up to a week or more.
Generally, it depends on many factors, including an individual’s diet and macronutrient ratios, activity level, and other factors such as age and genetics. However, despite being different for each person, reaching ketosis typically decreases over time as your body gradually adjusts.
When you significantly limit your carbohydrate intake, your body’s glycogen stores become depleted, and it starts to break down stored fat for energy. As your body switches to using fat for fuel, it produces ketones that fuel your brain and other organs.
If you are just starting your ketogenic journey, remember that achieving the desired ketosis may take longer than expected – but it’s possible with perseverance!

5 Signs on How To Know When You’re in Ketosis
- Increased ketones: One of the most reliable ways to confirm ketosis is to measure the levels of ketones in your blood, urine, or breath. Increased levels of ketones are a sign that your body is using fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
- Decreased appetite: Many people experience a decreased appetite when they enter ketosis, as ketones can help suppress hunger hormones.
- Increased energy: Once your body has adapted to using ketones for fuel, many people report increased energy levels and improved mental clarity.
- Improved physical performance: Some people report improved physical performance and endurance in ketosis, particularly during long-duration activities.
- Changes in urination: When your body is in ketosis, you may experience more frequent urination and increased thirst as your body tries to flush out excess ketones.
What to expect when you start keto: first changes in your appearance
When you start a ketogenic diet, you may notice some changes in your appearance within the first few weeks. Here are a few things you can expect:
- Weight loss
One of the most noticeable changes in appearance that people experience when starting a ketogenic diet is weight loss. The diet’s low-carbohydrate, high-fat nature can help reduce overall calorie intake and promote fat burning.
- Decreased bloating
Many people experience reduced bloating when starting a ketogenic diet. This is because the diet is low in carbohydrates, which can cause water retention and bloating.
- Clearer skin
Some people report clearer skin when following a ketogenic diet. The diet is typically low in processed foods and added sugars that can contribute to acne and other skin issues.
What foods put your body in ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which your body utilizes fat as fuel instead of carbohydrates. It has proven beneficial health effects and can affect weight loss efforts if youʼre on the right nutrition plan. However, to get into ketosis, you must pay close attention to the foods you consume.
A typical keto diet is based on high-fat, moderate protein, and low-carbohydrate intake.
Foods such as eggs, avocados, fatty fish like salmon, nuts, and nut kinds of butter, olive oil, cheese, and butter are excellent for putting your body into ketosis. If you’re short on time, other convenient options, such as ketogenic meal replacement shakes, can help get you into the desired metabolic state.
By consuming the proper macro-nutrient ratios of fats, proteins, and carbs daily, your body will start burning fat as fuel instead of glucose from carbohydrates.
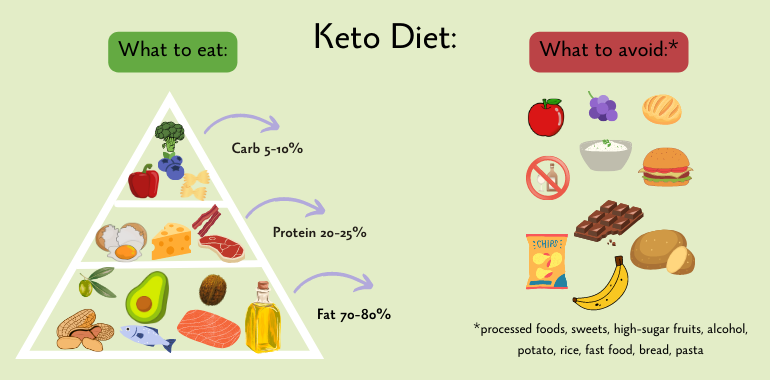
What Is the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is comprised of a low-carb, high-fat, and moderate protein food intake.
Foods to indulge on a ketogenic diet include:
- Low-carb veggies
- Cheese
- Healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and oils low in net carbs, such as olive oil and coconut oil
- Sources of protein such as poultry and eggs and other lean meats
- Plain Greek yogurt and cottage cheese
- Berries
- Dark chocolate and cocoa powder
As far as beverages, water, unsweetened coffee, and tea are recommended to aid in hydration and maintain energy during ketone metabolism. Whole or plant-based milk is also recommended for protein and calcium intake.
It is also essential to be aware of foods outside of a ketogenic diet that can cease the process of ketosis. This is because these foods are high in carbs, thus negating the process of ketosis.
Foods that should be avoided include:
- Processed foods, such as sweetened yogurt, chips, and crackers
- Honey, syrup, and sugar in any form
- Juices (natural or not) that are higher in carbs
- Grains such as cereal, crackers, rice, pasta, bread, and beer that are high in carbohydrates are also noted that even whole-wheat/bean-based pasta still holds high carb levels, although marketed as healthier alternatives.
Although beneficial to an extent, these are some of the foods that should be greatly limited during a ketogenic diet:
- Starchy vegetables, such as corn, potatoes, sweet potatoes, and beets –
These types of vegetables are higher in carbs and if not maintained, these starchy foods may alter ketosis.
- High-sugar fruits, such as bananas, raisins, dates, pears, and mangos –
These fruits may spike blood sugar and are also high in carbs.
How To Quickly Get into Ketosis – 3 Key Steps
Entering ketosis can take time and varies from person to person, but you can take a few steps to help your body transition into ketosis more quickly. Here are three key steps:
1. Restrict carbohydrate intake
Restricting your carbohydrate intake is an essential step to getting into ketosis quickly. To enter ketosis, most people must limit their carbohydrate intake to fewer than 50 grams daily. However, some people may need to restrict their carbohydrate intake to as little as 20 grams daily to achieve ketosis.
2. Increase healthy fat intake
Are ketones good for you? – Absolutely! Once you have restricted your carbohydrate intake, increasing your intake of healthy fats is essential. This will provide your body with the necessary fuel to transition to using fat for energy. Good sources of healthy fats include nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish.
3. Incorporate moderate protein intake
While protein is an essential nutrient, too much protein can hinder ketosisTherefore, it’s important to incorporate moderate protein intake into your diet. You should aim for 0.6-1 gram of protein per pound of lean body mass daily. This will help prevent muscle loss while allowing your body to enter ketosis.
Who Should NOT Do the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is not for everyone. Because it is highly restrictive by nature and can alter body chemistry, here are populations who should not indulge in the keto diet or attempt ketosis:
- Nursing or pregnant women
- People with type 1 diabetes
- People with pre-existing metabolic conditions
- People with pre-existing liver, pancreatic, or kidney damage.
What You Should Know About Keto Starvation Mode
Keto starvation mode is a term used to describe a situation in which the body’s metabolism slows down during a ketogenic diet due to a lack of sufficient calories or nutrients. When the body is deprived of carbohydrates, its primary energy source, it begins to burn stored fat for fuel. This process is known as ketosis.
- It may happen if you eat less
To enter and maintain ketosis, you must consume very few carbohydrates and moderate amounts of protein. However, you must also ensure you eat enough calories to support your body’s essential metabolic functions.
- It can be prevented
You can avoid keto starvation by eating enough calories and nutrients to support your body’s essential metabolic functions. 
Ketone vs Glucose: Which Is a Better Source of Brain Fuel?
The brain can use ketones and glucose for fuel, but they have different metabolic pathways and may be preferable in other circumstances.
Glucose is the primary source of energy for the brain under normal conditions. Glucose is readily available from the carbohydrates in our diet and is transported across the blood-brain barrier by glucose transporters. In addition, the brain uses glucose to produce ATP, which is the primary energy currency of the cell.
On the other hand, during low carbohydrate intake or fasting periods, the liver produces ketones from fatty acids. The brain can also use ketones for energy, and they may even be a preferred fuel source for certain brain functions, such as cognitive processing and memory formation.
General Benefits of Ketosis – Why Try
The benefit of ketones is space for reducing cholesterol, which can improve cardiovascular health, metabolic disease, and the risk of diabetes.
Additional benefits include:
- Weight loss – Which can occur on behalf of ketones
- Increased energy – Ketones can improve the body’s mobility by aiding in muscle development and cell regeneration
- Increased focus – This can result on behalf of increased protein, which may influence brain development

The Keto Advantage For Fat Loss
The Keto diet offers several advantages when it comes to fat loss. First, by promoting increased production of ketones and using fatty acids as the primary energy source, the Keto diet forces the body to use stored fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This can lead to rapid fat loss.
Additionally, when following a Ketogenic diet, appetite is often suppressed, helping individuals who struggle with overeating by curbing hunger pangs. On top of that, research suggests that being on the Keto diet helps preserve muscle mass while reducing body fat stores, which is essential for keeping metabolism at healthy levels long-term.
Adopting a Ketogenic lifestyle may be the key to shedding unwanted weight and regaining your ideal physique.
Symptoms of Ketosis
Ketosis is defined as the presence of ketones in the body. Weight loss is a common symptom of ketosis as weight loss can occur in the first week. Initially, weight loss constitutes stored carbs and water in the body. Weight loss can occur with the additional symptom of appetite reduction in which one’s increased protein and vegetable intake can result in feeling fuller at a faster rate.
Other symptoms that may occur include:
- “Keto Flu”, which describes the body’s changes during the onset of ketosis including fatigue, irritability, nausea, difficulty sleeping, and constipation
- “Keto-Breath” is described as a fruity or sour smell that can occur due to a change in diet
Ketosis fat-burning rate helps you monitor weight loss
Monitoring your body’s natural fat-burning rate is one of the most efficient ways to measure weight loss. When your body enters a state of ketosis, it shifts its primary fuel source away from carbohydrates to fat and other ketones.
By understanding the link between a higher fat-burning rate and decreased caloric intake, you can be sure your dieting efforts will pay off. In addition, studies have shown that those who nutrition monitor their bodies entering into ketosis are more likely to reach their weight loss goals than those who don’t.
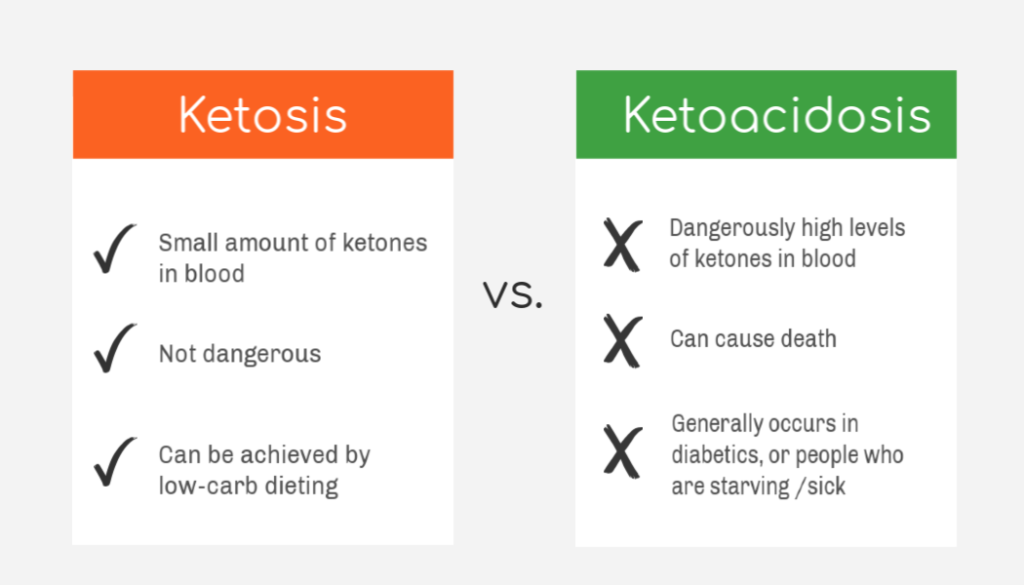
Ketoacidosis Awareness
When ketone levels get too high, ketoacidosis can occur. Ketoacidosis is a dangerous condition that can happen, typically in individuals with diabetes, and can be triggered due to illnesses that cause higher levels of hormones that work against insulin. Because the keto diet increases these ketones, monitoring symptoms and the level of ketones in the blood and urine is essential. Ketoacidosis tests can help detect ketone levels and can be done in medical settings and at home.
Is Keto Bad For Your Liver?
The ketogenic diet has been shown to have both positive and negative effects on liver health, depending on the individual and the specific circumstances. Here are some things to consider:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Studies have shown that a low-carb, high-fat diet can help reduce liver fat and improve liver health markers in individuals with NAFLD.
- Liver function tests: Some studies have reported temporary increases in liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, during the early stages of a ketogenic diet.
- Gallstones: Rapid weight loss, which can occur during the early stages of a ketogenic diet, has been associated with an increased risk of gallstones.
Does Drinking Water Reduce Ketones – Destroying This Myth
There is a common myth that drinking water can reduce ketones or even “flush out” ketones from the body, but this is not accurate.
Drinking water is essential for maintaining hydration and overall health, and it does not directly affect the body’s production or level of ketones. Ketones are produced by the liver when carbohydrate intake is low, and the body uses them for energy.
Drinking water can be beneficial for individuals following a ketogenic diet. The ketogenic diet can cause dehydration due to the diuretic effect of ketones, and drinking water can help prevent this. Additionally, staying hydrated can help reduce feelings of hunger and support overall weight loss efforts.
Why Can’t I Get into Ketosis – Eating Low Carbs Without Results
There could be some reasons why you cannot get into ketosis, even if you are eating a low-carb diet. Can stress kick you out of ketosis? Here are some potential explanations:
- You’re still eating too many carbs.
To get into ketosis, you must restrict your carbohydrate intake to 20-50 grams daily.
- You are overeating protein.
When you consume too much protein, your body can convert it into glucose through gluconeogenesis, preventing you from achieving ketosis. Limit your protein intake to around 1 gram per kilogram of body weight.
- You aren’t eating enough fat.
To enter ketosis, your body must shift from burning glucose for energy to burning fat. Your body may need more fuel if you need to consume more fat.
- You need to give it more time.
It can take several days or even a week or more for your body to transition into ketosis fully. Give it some more time, and continue to monitor your progress.
- You have a medical condition.
Certain medical conditions can sometimes interfere with ketosis. For example, if you have a metabolic disorder that affects your ability to process fats, you may have difficulty entering ketosis.











I am glad that thanks to deep ketosis, you can get clear skin. How long do I need to follow the diet to see results?
Hi, Mia 😊
Results may vary, but many people start noticing changes in their skin within a few weeks of following the diet. Hope you see the results you’re looking for soon!